A Strategic Legal Consultancy Firm
• 100+ years of collective experience of the Founders • Interdisciplinary expertise on Civil, Criminal, Technology and AI related laws • Advisors to Corporates and NRIs
NRIs often need a Trusted Legal partner in India
Support NRIs and International Corporates on a variety of leagl issues
• Inheritance (property disputes) • Family Law (Cross border issues, family counselling and divorce etc) • Comprehensive Legal Support to Corporates
Securing Your Intellectual Wealth
IPR laws protect your intellectual wealth
• IPR concept to execution • Strategic guidance • Expertise in Litigation and Alternative Dispute Resolutions
Corporate Legal Strategy
Strategic Advisers for
• Contract Management and Vetting • Litigation and Disputes • Employment and Labor Laws
Awards & Recognitions
Best Law Firm Award
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis.
Best Law Firm Award
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis.
Best Law Firm Award
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis.
Best Law Firm Award
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis.
Best Law Firm Award
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis.
Best Law Firm Award
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis.
Our Practice Areas

BANKING & FINANCIAL SERVICE
Given the present Volatile, Uncertain, Complex and Ambiguous (VUCA) environment affecting the borrowers and lenders..... Read More
BUSINESS & TRADE LAWS
With the technological advancements the both the opportunities and challenges have increased many folds before the businesses........ Read More
TECHNOLOGY LAWS
In today’s world no business or industry can operate without the aid of the technology. Therefore, interaction with the Technology is inevitable.......Read More
CORPORATE LAW
Our Corporate Law Practise covers the entire spectrum of the domain through cutting edge legal solutions for the dynamic Corporate Structure of the present Industry...... Read More
REAL ESTATE
We have deep experience in the domain and have extensive background of working across high stake real estate litigation and property management.....
Read More
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY LAWS
Our specialized team of Technology Experts, Creative individuals and Lawyers puts in an unique position to support our clients with their Intellectual Property needs...... Read More
LITIGATION & DISPUTE RESOLUTION
Our Litigation and Dispute Resolution Practice has been the oldest and well-known area of the practise. Our founder has impeccable track record of the executing litigation strategies for the high stake disputes.....Read More
FAMILY LAWS
The Family Law of NyayaNiti is a superior Indian federal court of law which deals with family law matters, such as divorce applications, parenting disputes, and the division of property when a couple separate.....Read More
About Us+
Awarded Law Firm of the Year
Nyaya Niti is a full service and interdisciplinary Law Firm, headquartered at Pune. We support our clients with domain-specific legal expertise, vast experience of the procedural aspects clubbed with cutting edge technological advances.
Nyaya Niti – A Strategic Legal Consultancy LLP is built upon an enduring legacy of over 45 years, bolstered by the collective expertise of our founders, who bring together more than 100 years of specialized legal and technology experience.
Our Civil Practice covers an extensive range of complex matters, including intricate land disputes, sophisticated intellectual property conflicts, challenging banking litigation, corporate law compliance issues, and the disputes arising therein. Our seasoned team is adept at navigating through these multifaceted issues, delivering precise and strategic solutions tailored to the specific needs of our clients.
Best Legal Advice

Our Practice Areas
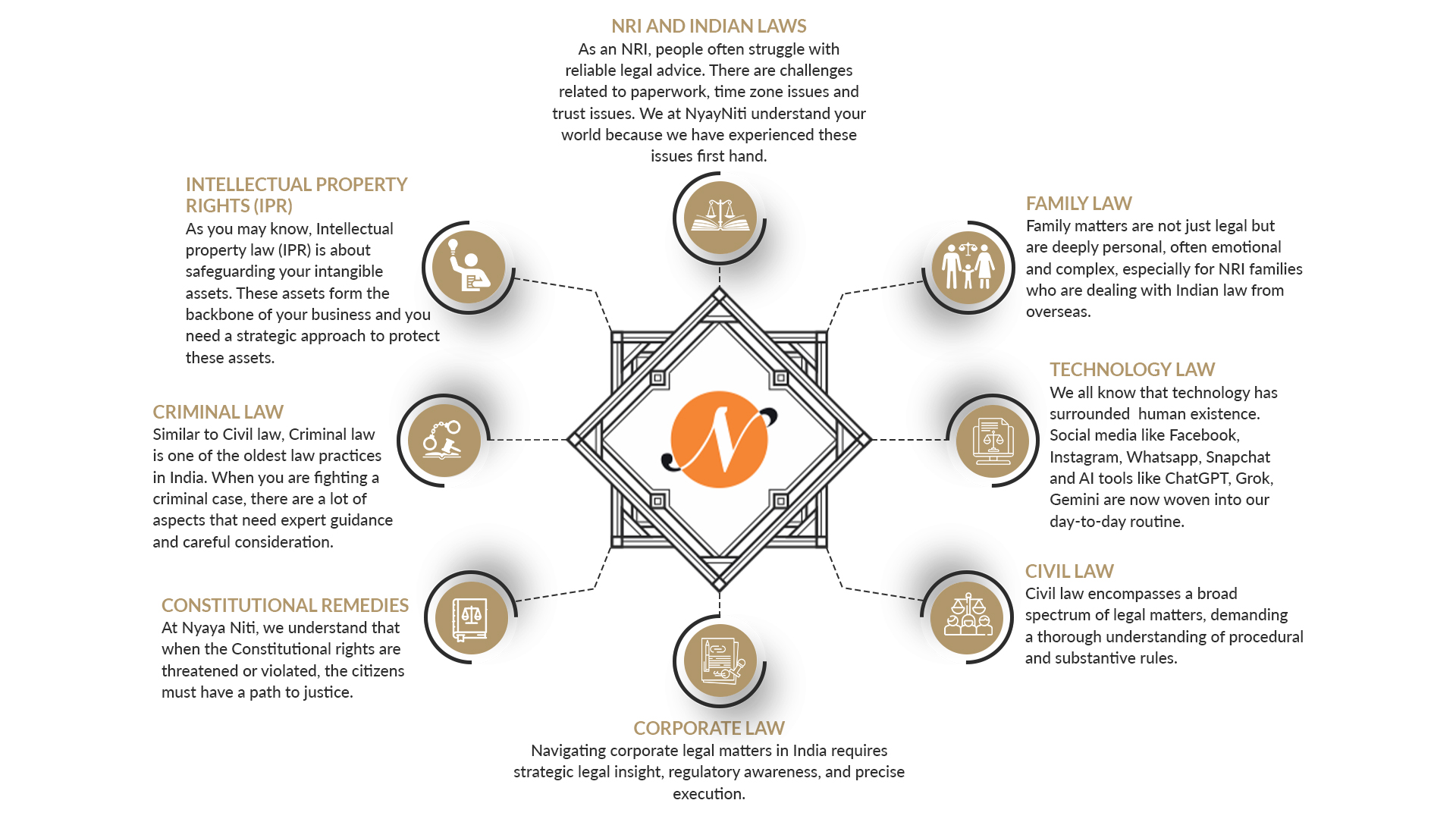


NRI AND INDIAN LAWS
As an NRI, people often struggle with reliable legal advice. There are challenges related to paperwork, time zone issues and trust issues. We at NyayNiti understand your world because we have experienced these issues first hand. Read More
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS (IPR)
As you may know, Intellectual property law (IPR) is about safeguarding your intangible assets. These assets form the backbone of your business and you need a strategic approach to protect these assets. Read More
CRIMINAL LAW
Similar to Civil law, Criminal law is one of the oldest law practices in India. When you are fighting a criminal case, there are a lot of aspects that need expert guidance and careful consideration. Read More
CONSTITUTIONAL REMEDIES
At Nyaya Niti, we understand that when the Constitutional rights are threatened or violated, the citizens must have a path to justice. Read More
Educational Law
Key Issues: Fee regulation, employment disputes, curriculum grievances
Our Services : Legal representation for students and educators, regulatory compliance guidance
Read More
Family Law
Key Issues: Divorce, custody disputes, inheritance conflicts
Our Services : Mediation, legal drafting, and court representation
Read More
Land Law
Key Issues: Title disputes, encroachments, land acquisition issues
Our Services : Land survey assistance, partition suit representation, zoning compliance advisory
Read More
FAMILY LAW
Family matters are not just legal but are deeply personal, often emotional and complex, especially for NRI families who are dealing with Indian law from overseas. Read More
TECHNOLOGY LAW
We all know that technology has surrounded human existence. Social media like Facebook, Instagram, Whatsapp, Snapchat and AI tools like ChatGPT, Grok, Gemini are now woven into our day-to-day routine. Read More
CIVIL LAW
Civil law encompasses a broad spectrum of legal matters, demanding a thorough understanding of procedural and substantive rules. Read More
CORPORATE LAW
Navigating corporate legal matters in India requires strategic legal insight, regulatory awareness, and precise execution. Read More
COOPERATIVE LAW
While the roots of Cooperative law go as far as 1904, in today’s age, there are a lot of challenges presented by emerging population growth and changes in the family structures. Read More
Constitutional Law
Key Issues: Rights violations, federal disputes, election conflicts
Our Services : Filing constitutional petitions, rights defense, policy advisory
Read More
Employment Law
Key Issues: Workplace discrimination, wrongful termination, wage disputes
Our Services : Employment contract drafting, labor tribunal representation, labor law compliance
Read More
Housing Law
Key Issues: Possession delays, tenant-owner conflicts, RERA violations
Our Services : Representation in housing disputes, tenancy agreement drafting, RERA compliance assistance
Read More
How It Works

Consultation
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Donec velit neque.

Strategize
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Donec velit neque.

Take Action
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Donec velit neque.
Office Locations
Pune
507, Fortuna, Near Shivar Chowk, Pimple Saudagar, Pune – 411027
Aurangabad
Chh. Sambhaji Nagar: 4/5 A, Vedant Gruhkul, Near Deogiri Bank, Darga Road, Chhatrapati Sambhaji Nagar (Aurangabad) – 431001
Mumbai
Mumbai: 6, Mezzanine Floor, Rustom Building, V. N. Road, Mumbai, 400001
What Our Clients Say

I am one of the Clients. Excellent services, coordination and success rate. I wish Nyayaniti legal all the success.
Abhishek

The Firm has an organized and sophisticated work culture where each member is aware of his/her role and responsibilities.
Rahul

Nyayaniti is one of the best law firms in India. They provide excellent client services with professionalism and proficiency.
